Insulinoma,
Cystic fibrosis, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and Pancreatic Cysts. Strange
names, but they have one thing in common, all of them involves the pancreas. Pancreas
has two important functions in digestion a) first, it is responsible for the
productions of enzymes to digest food and b) It produces hormones that control
blood sugar. It makes insulin and glucagon, two important hormones that control
blood sugar.
Insulinoma,
Cystic fibrosis, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and Pancreatic Cysts. Strange
names, but they have one thing in common, all of them involves the pancreas. Pancreas
has two important functions in digestion a) first, it is responsible for the
productions of enzymes to digest food and b) It produces hormones that control
blood sugar. It makes insulin and glucagon, two important hormones that control
blood sugar.
Now, imagine if laboratory tests are not discovered. How can
you diagnose these Out-Of-This-World-Names-Of-Diseases. Thanks to those geniuses
who discovered these machines and laboratory tests we are using now.
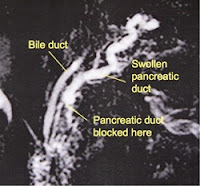
1) Endoscopic retrograde
cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
 Who doesn't love eating? but did you know that every meal, bile enters the small
intestine where it breaks down fats. Healthy gallbladder keeps bile from
flowing, however, when the gallbladder becomes diseased, the flow slows.
Chemicals which exist in the gallbladder solidify into either one large stone
or several small ones.
Who doesn't love eating? but did you know that every meal, bile enters the small
intestine where it breaks down fats. Healthy gallbladder keeps bile from
flowing, however, when the gallbladder becomes diseased, the flow slows.
Chemicals which exist in the gallbladder solidify into either one large stone
or several small ones.ERCP is a procedure used to identify stone, tumors or narrowing in the bile ducts. This is the most reliable way of diagnosing and treating ductal stones. If gallstones are blocking the bile duct, they can also be removed during an ERCP.
- The endoscope is inserted through the mouth.
- It is passed through the esophagus and stomach until it reaches the duodenum.
- A catheter is passed through the endoscope and inserted into the ducts that lead to the pancreas and gallbladder.
- A special dye is injected into these ducts, and x-rays are taken. Dye is used to help the doctor see the structure of the common bile duct, other bile ducts, and the pancreatic duct on an X-ray.
2) Magnetic resonance
cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Sounds familiar eh? I know you already know MRI, and MRCP is a kind
of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) that is used to view the bile ducts and the
pancreatic duct.
The name is a bit difficult to pronounce but it is a non-invasive method. It is performed when Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has failed or cannot be done. It does not require contrast for imaging the pancreaticobiliary tree and may also be as good as contrast enhanced CT for assessing the severity and detecting pancreatic necrosis in patients with acute pancreatitis (Baker, S. 2004).
The name is a bit difficult to pronounce but it is a non-invasive method. It is performed when Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has failed or cannot be done. It does not require contrast for imaging the pancreaticobiliary tree and may also be as good as contrast enhanced CT for assessing the severity and detecting pancreatic necrosis in patients with acute pancreatitis (Baker, S. 2004).
3) Abdominal CT with
contrast enhancement

Contrast Enhance Computed Tomography is the gold standard for diagnosing pancreatic necrosis and peripancreatic collections. Contrast-enhance CT can also differentiated mild acute pancreatitis from severe acute pancreatitis. It is often performed between 3 and 10 days of the onset of symptoms to grade the severity of the disease (Baker, S. 2004).
4) Fecal Elastase Test (FET)
.jpg) Fecal=Feces=Poopoo=Yuck! but we also have to test the poopoo becuase it contains the enzyme elastase. Elastase is an enzyme found
in fluids produced by the pancreas. The fecal elastase test is another test of
pancreas function.
Fecal=Feces=Poopoo=Yuck! but we also have to test the poopoo becuase it contains the enzyme elastase. Elastase is an enzyme found
in fluids produced by the pancreas. The fecal elastase test is another test of
pancreas function."FET is a simple and accurate functional test for CP, and it is hardly influenced by extrapancreatic disorders or therapy with exogenous enzymes" (Gastroenterol, A.J. 1995).
The test measures the levels of elastase
and is used to
diagnose certain pancreas disorders related to not producing enough digestive
enzymes.
5) Amylase and Lipase
test
Being a medical technology student. We should embrace, love and be used to seeing blood. It is important to have the skills in collecting blood because there are a lot of tests that require blood samples. example of those tests are amylase and lipase test.
Amylase and lipase test are often ordered at the same time. These tests help in diagnosing and monitoring acute and chronic pancreatitis and other problems and disorders that involve the pancreas. The two tests may also be tested using urine sample.
Amylase and lipase test are often ordered at the same time. These tests help in diagnosing and monitoring acute and chronic pancreatitis and other problems and disorders that involve the pancreas. The two tests may also be tested using urine sample.
For more information, watch this video:
Reference/s:
Baker, S. 2004. Diagnosis
and Management of Acute Pancreatitis
Gastroenterol. A.J.
1995. Fecal elastase test: evaluation of a new noninvasive pancreatic function
test.
http://www.medicinenet.com/endoscopic_ultrasound/article.htm
Photo credits:
.jpg)